双曲線関数とは
双曲線関数 (英:hyperbolic function) とは、単位円に対応する双曲線に関わる次図面積を 2θ とした際の各関数を指す。なお次図の場合、x=coshθ, y=sinhθ で定義される。
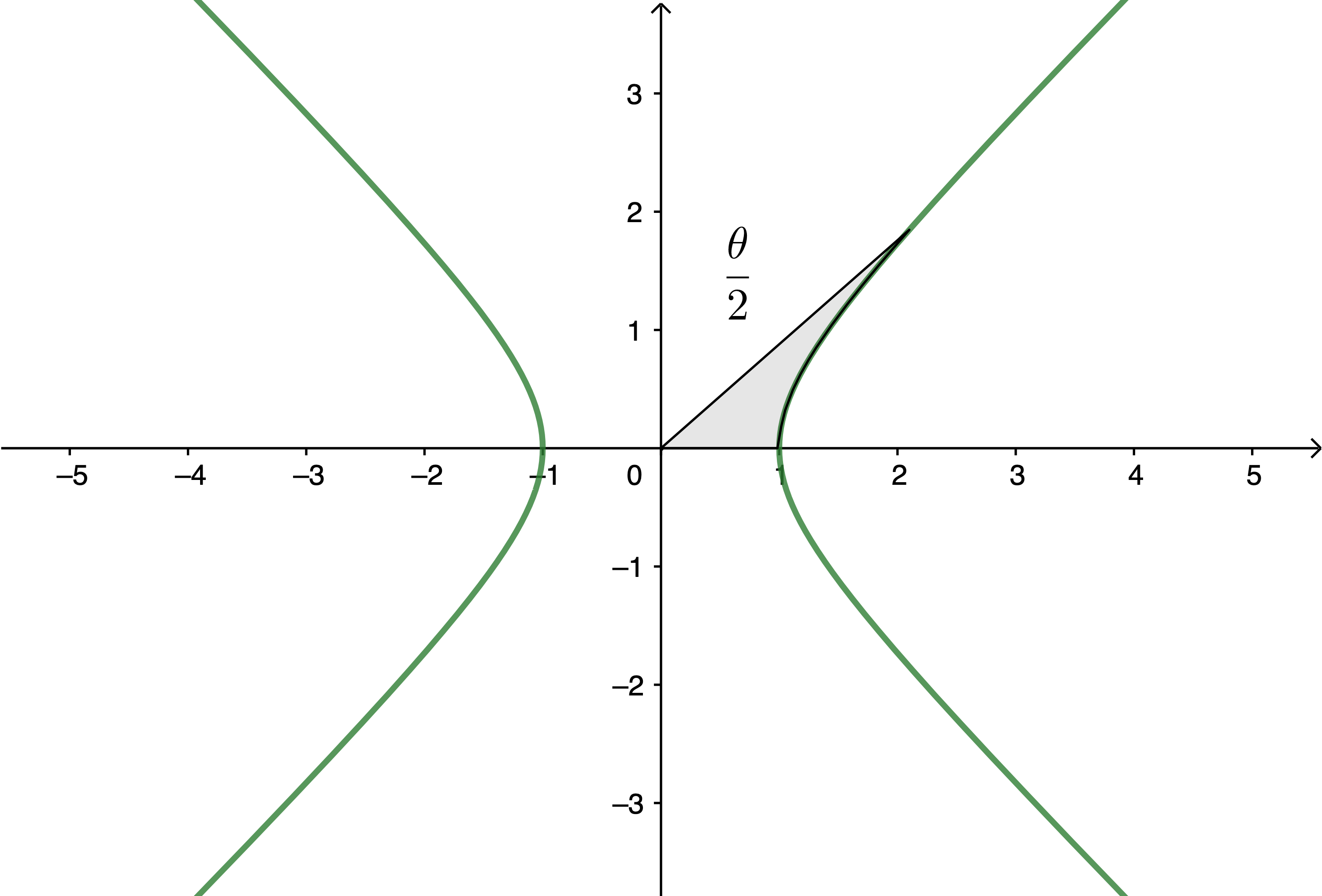
双曲線余弦関数
coshθ=2eθ+e−θ
双曲線余弦関数の導出:
上図より、
2θ=2xx2−1−∫1xt2−1dt∵x2−y2=1(1)
右項の不定積分を F とすると、
F(t)2F(t)F(t)=∫t2−1dt=∫(t)′t2−1dt=tt2−1−∫t(t2−1)′dt=tt2−1−∫t2−1t2dt=tt2−1−∫t2−1(t2−1)+1dt=tt2−1−∫t2−1dt−∫t2−11dt=tt2−1−F(t)−ln∣∣∣∣t+t2−1∣∣∣∣+C=tt2−1−ln∣∣∣∣t+t2−1∣∣∣∣+C=21(tt2−1−ln∣∣∣∣t+t2−1∣∣∣∣+C)(2)
(1),(2) から、
2θθeθ=2xx2−1−∫1xt2−1dt=2xx2−1−F(x)+F(1)=2xx2−1−21(xx2−1−ln∣∣∣∣x+x2−1∣∣∣∣)=21ln∣∣∣∣x+x2−1∣∣∣∣=ln∣∣∣∣x+x2−1∣∣∣∣=x+x2−1(3)
(3) から、e−θ を得る。
e−θ=x+x2−11=(x+x2−1)(x−x2−1)x−x2−1=x−x2−1(4)
(3),(4) より、
eθ+e−θx∴coshθ=2eθ+e−θ=2x=2eθ+e−θ
双曲線正弦関数
sinhθ=2eθ−e−θ
双曲線正弦関数の導出:
双曲線余弦関数の導出から、
eθ−e−θy∴sinhθ=2x2−1=2y∵x2−y2=1=2eθ−e−θ=2eθ−e−θ
関連記事